Bid vs ask price is an important concept in trading the financial markets. The asking price is the lowest price a brokerage is willing to sell a stock, while the bid price is the highest price a trader is willing to pay to purchase it. These concepts also apply in crypto trading since tokenized assets are similar to stocks.
Table of Contents
In this article, we’ll learn what is the bid and ask price, bid and ask price examples, the difference between the bid and ask price, and the factors that influence the bid and ask price.
What is the bid price?
The two-way price quote known as “bid and ask” or “bid and offer” indicates the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a security and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. One important measure of the asset’s liquidity is the spread, or the gap between the ask and bid prices. Generally speaking, higher liquidity results from a lower spread.
If a stock has a $20 bid price, for example, it indicates that a buyer is prepared to acquire the shares at that amount. The bid price, which represents the demand side of the market equation, is a crucial component of order books.
What is the ask price?
The lowest amount a seller will take for a security is the ask price, often referred to as the offer price. Similar to the bid price, the ask price is a crucial component of the order book and represents the supply side of the market. It represents possible purchasing prices for traders or investors who are interested.
Similar to the bid price, supply and demand dynamics, mood, market liquidity, and volatility all affect the ask price. A security’s ask price may drop if its supply grows or if demand declines.
As a result of sellers’ perceptions of heightened risk, a highly volatile market may also result in a higher ask price.
Now that we have explained the bid and ask price, let’s discuss the bid-ask spread in detail.
The bid-ask spread: explained
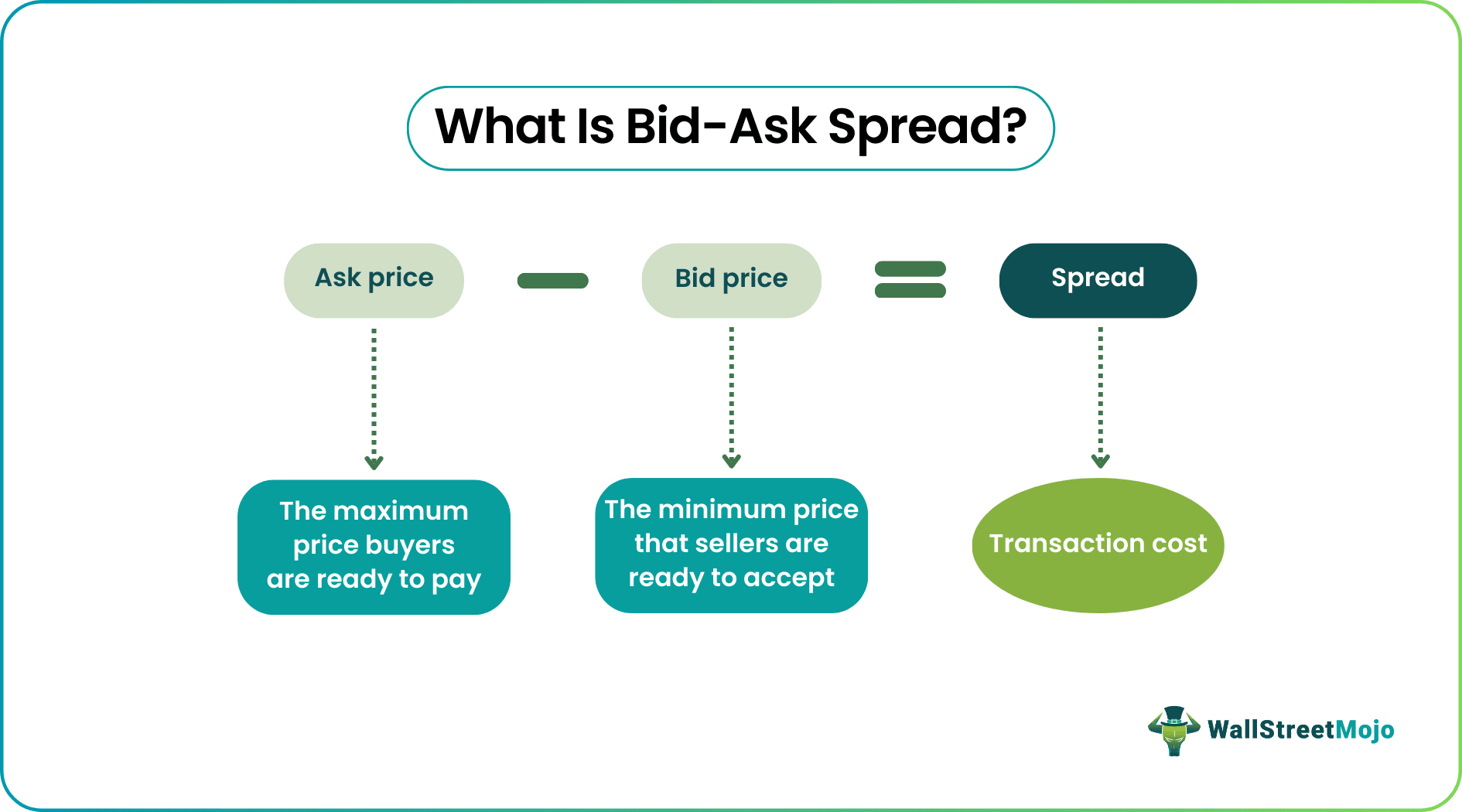
The difference between the bid and ask prices is referred to as the spread. An exchange with low spreads usually has good liquidity and is less susceptible to induced volatility from low trading volume.
The bid-ask spread is the difference between the maximum amount a buyer is willing to pay for a financial instrument (the bid price) and the lowest amount a seller is willing to accept for it (the ask or offer price).
There is usually plenty of liquidity in the security when the ask and bid prices are extremely close. The security is considered to have a “narrow” bid-ask spread in this situation. Investors may benefit from this circumstance as it makes it simpler to enter or leave their holdings, especially when holding sizable stakes.
However, trading assets with a “wide” bid-ask spread—where the ask and bid prices are far separated—can be costly and time-consuming.
Example: understanding the bid-ask spread in action
For example, if a security has a bid price of $20 and an ask price of $22, the bid-ask spread is $2 ($22 – $20 = $2). This $2 is the difference between the price a seller is willing to sell the security for and the amount a buyer is willing to pay for it.
Factors influencing the bid-ask spread
Volatility is another significant factor that influences the bid-ask spread. Generally speaking, volatility rises when the market is rapidly declining or rising. Due to market makers’ desire to exploit and benefit from the bid-ask gap, it is significantly wider during these periods. Investors are more eager to pay for assets with rising values, which allows market makers to raise premiums. The bid-ask spread is small when there is little volatility and little risk or uncertainty.
The bid-ask spread is also influenced by the price of a stock. The bid-ask spread will often be greater when the price is low. This has to do with the concept of liquidity. The majority of inexpensive securities are either little or brand-new. As a result, these securities are less liquid since there is a cap on the quantity that may be exchanged.
In the end, supply and demand determines the bid-ask spread. In other words, a lower spread will result from tighter supply and stronger demand. Nowadays, it’s much easier to find a buyer or seller thanks to technology.
Bid-Ask spread in cryptocurrency markets
Knowing what is the bid and ask price is essential for making wise investing choices in the realm of cryptocurrency trading. Traders may better navigate the cryptocurrency market, analyze market conditions, and estimate transaction costs by understanding the dynamics of bid and ask prices and their connection. Traders may make educated judgments and modify their strategy by closely monitoring the bid/ask spread.
Keep in mind that the gap between the highest price a buyer is ready to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to take is known as the bid/ask spread. The spread may be impacted by variables including currency rates, market volatility, trading volume, and market liquidity.
When making transactions, traders should take transaction costs into account and keep an eye on the bid/ask spread to assess market conditions. Traders may improve their trading tactics and perhaps increase their profitability in the crypto market by comprehending and using this idea.
What is a good bid-ask spread?
A good bid-ask price spread is narrow, meaning it should not be more than a few cents or fractions. This narrowness in bid-ask price is known as a spread, and the lower the spread, the higher the liquidity of the asset, which is easier to trade for investors.
How to calculate bid-ask spread percentage?
The bid-ask spread percentage can be calculated by subtracting the bid price from the ask price dividing that by the mid-price, and then multiplying it by 100.
This article first appeared at crypto.news
